


Next: Some Matching Case Studies
Up: Model Based Object Recognition
Previous: Model Based Object Recognition
Basic approach:
- Nodes of the tree represent a scene to model primitive (e.g. edge,
surface) match.
- Let Tree have m branches at each node that correspond to model
primitives.
- Let level of tree represent a model primitive.
- The level and node position specify a match pair.
- Use a tree searching strategy (see below for methods used) to find a match.
- One traversal through tree gives a match list -- a possible match
of scene to model features.
- Representation called a search or interpretation tree.
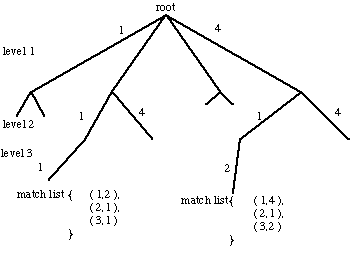
Fig.  Interpretation tree
Interpretation tree
How do we perform matching?
- At each level of the tree, one of the edges from the scene is matched
with each of the m possible edges in the model.
- Each node has m children
representing taking the match proposed so far together with all possible matches
for the current scene
edge.
- A transformation representing the match so far can be maintained.
- Search tree in depth first manner and pruned by
rejecting interpretations that fail to satisfy current match.
- The search space is large --
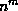 possible combinations for n scene
primitives.
possible combinations for n scene
primitives.
- A lot of computations?
We can reduce the computational overheads by employing some local geometric
constraints to prune the tree further.
These are:
- Cheap to compute and employ.
- applied before the transformation test.
For Edges we could employ:
- Distance Constraint
- -- The length of the sensed edge must be less than
or equal to the length of the model edge under consideration.
- Angle Constraint
- -- The angle between two adjacent sensed edges must
agree with that between the two corresponding matched model edges.
- Direction Constraint
- -- Let
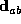 represent the range of
vectors from any point on sensed edge a to any point on sensed edge b. In an
interpretation which respectively pairs sensed edges a and b with model edges
i and j, this range of vectors must be compatible with the range of vectors
produced by i and j.
represent the range of
vectors from any point on sensed edge a to any point on sensed edge b. In an
interpretation which respectively pairs sensed edges a and b with model edges
i and j, this range of vectors must be compatible with the range of vectors
produced by i and j.
For Surface we could employ:
- Angles between planes.
- Area of planes.
- Invariants.
- Measures of curvature.



Next: Some Matching Case Studies
Up: Model Based Object Recognition
Previous: Model Based Object Recognition
dave@cs.cf.ac.uk
