


A Beginner's Guide to Computational Thinking
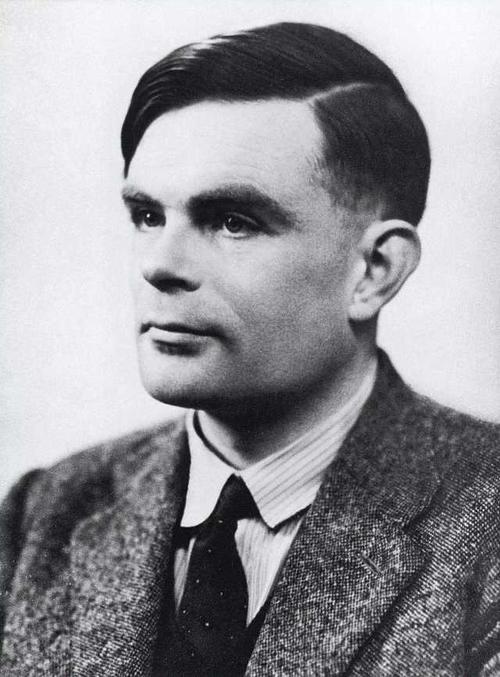
Turing was born in Maida Vale, London on June 23, 1912. He was an outstanding mathematician, logician and computer scientist. He left an indelible mark on mathematics, cryptography, and computing, and contributed to subsequent fields such as computer science, cognitive science, artificial intelligence, and artificial life. Turing published his most important theoretical work "On Computable Numbers and Their Application to Entscheidungsproblems (Decision Problems)" in 1936. This article describes the abstract digital computer on which modern computers are based - now simply called the Universal Turing Machine - which laid the foundation for modern computer science. It is still the basis of today's computer systems. He completed his PhD in 1938,entitled 'Systems of Logic Based on Ordinals, subsequently published under the same title (Chapter 3, with further exposition in Chapter 4). Now a classic, this work addresses the implications of Gödel's famous incompleteness result. During World War II, Turing's expertise in cryptography also played a huge role. It was of great help in deciphering the Enigma machine code used by Germany at the time. He enabled the Allied forces to intercept enemy information and Can decode encrypted messages. This intelligence was also important to the end of the war. After the war, Turing continued to make great contributions. He designed the Automatic Computing Engine (ACE), one of the earliest storage computers in human history. His research in artificial intelligence also led to the development of the "Turing Test". While waiting for engineers to build the ACE, Turing and his team pioneered the science of computer programming, writing a library of complex mathematical programs for the planned machine. Sadly, Turing's life was marked by social prejudice and he was persecuted for being gay. Mr. Turing died on June 7, 1954, at the age of 41. Mr. Turing's life was very brilliant. He was praised in various fields. His legacy helped the development of mankind in all aspects, including computer science, and reflected the power of human innovation.
reference
Turing, A.M. 2004. The essential Turing [Online] Available at: https://librarysearch.cardiff.ac.uk/permalink/44WHELF_CAR/1fseqj3/alma9911763223102420 [Accessed: 24 October 2023].
Turing, S. 1970. Alan M. Turing: Turing, Sara, 1881-1976 : Free Download, borrow, and streaming [Online] Available at: https://archive.org/details/alanmturing0000turi_z0y2 [Accessed: 26 October 2023].