


Next: 3D imaging
Up: Image Acquisition
Previous: Image Acquisition
The basic
two-dimensional image is a monochrome (greyscale)
image which has been digitised.
Describe image as a two-dimensional light intensity function f(x,y) where x and
y are spatial coordinates and the value of f at any point
(x, y) is proportional to the brightness or grey value of the
image at that point.
A digitised image is one where
- spatial and greyscale values have been made discrete.
- intensity measured across a regularly spaced grid in
x and y directions
- intensities sampled to 8 bits (256 values).
For computational purposes, we may think of a
digital image as a two-dimensional array where x and y index
an image point. Each element in the array is called a pixel
(picture element). See Figs. 30 and 31.

Fig.  Greyscale image and highlighted region
Greyscale image and highlighted region
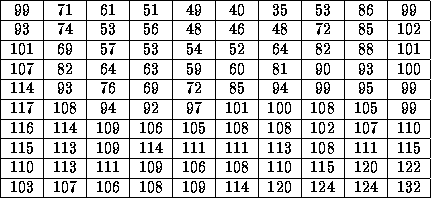
Figure: Pixel values in highlighted region
2D Input Devices
TV Camera or Vidicon Tube
A first choice for a two-dimensional image input device
may be a television camera -- output is a video signal:
- Image focused onto a
photoconductive target.
- Target scanned line
by line horizontally by an electron beam
- Electric current produces as the beam passes over target.
- Current proportional to the intensity of light at each
point.
- Tap current to give a video signal.
This form of device has several disadvantages.
- Limited resolution
- -- finite number of scan lines (about
625) and frame rate (30 or 60 frames per second)
- Distortion
- --
- unwanted
persistence between one frame and the next
- Non-linear video output with respect to light intensity.
- Non-flat target on tube.
CCD Camera
By far the most popular two-dimensional imaging device
is the charge-coupled device (CCD) camera.
- Single IC device
- Consists of an array of photosensitive
cells
- each cell produces an electric current dependent on
the incident light falling on it.
- Video Signal Output
- Less geometric distortion
- More linear Video output.
Frame Stores
Video Signal must be digitised.
A device known as a frame storeor
frame grabber usually performs this task. It:
- Digitises the incoming video signal
- Samples signal into discrete pixels at appropriate
intervals -- line by line.
- Samples signal into a (8 bit) digital value.
- Stores sample frame own memory.
- Frame easily transferred to computer memory or a
file.



Next: 3D imaging
Up: Image Acquisition
Previous: Image Acquisition
dave@cs.cf.ac.uk

![]() Greyscale image and highlighted region
Greyscale image and highlighted region
