

Next: About this document
Up: Model Based Recognition
Previous: Relaxation Labelling Methods
- Object model and scene features are represented in a
relational graph structure:
- a popular way of
representing and recognising objects in computer vision
A graph consists of
- a
set of nodes connected by links (also called edges
or arcs).
- Each node represents an object feature (for example, a
surface)
- Nodes can be labelled with several of the feature's properties (such as
size, shape, area, compactness, type of surface etc.).
- Links of the graph represent relationships between features - e.g.
- Distance between centroids of the features,
-
Adjacency of the features -- the ratio of the length of
the common boundary between the two features to the
length of the perimeter of the first-named feature.
- Boundary
representation model can be represented as this kind of graph.
object.
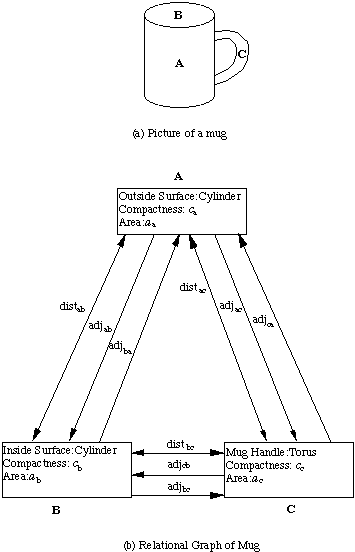
Fig. 52 Picture of a mug and its simple graph representation
Note that some
relationships are two-way, such as distance, in that the relation does not
depend on the direction of the link.
Other relations, such as adjacency, do depend
on the direction.
Recognition:
- A matter of matching two graphs -- Graph of the object model to the graph
of the scene containing the object.
- Matching methods must take into account
occlusion and overlapping objects.
- A graph derived from a solid model of
the mug would contain the bottom which is missing from the view shown (and
scene model).
- So the problem is that of finding a
subgraph of the complete graph derived from the solid model.
- This is a large search space problem -- Use Constraints.
- Graph theory a big topic in its own right.
 David Marshall 1994-1997
David Marshall 1994-1997
