The basic two-dimensional image is a monochrome (greyscale) image which has been digitised.
Describe image as a two-dimensional light intensity function f(x,y) where x and y are spatial coordinates and the value of f at any point (x, y) is proportional to the brightness or grey value of the image at that point.
A digitised image is one where
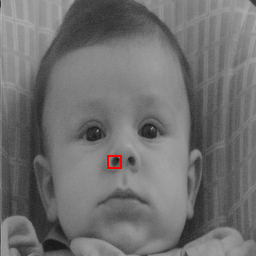
For computational purposes, we may think of a digital image as a two-dimensional array where x and y index an image point. Each element in the array is called a pixel (picture element). See Figs. 1 and 2.
Fig. 1 Greyscale image and highlighted region
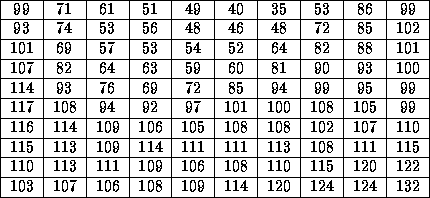
Figure: Pixel values in highlighted region