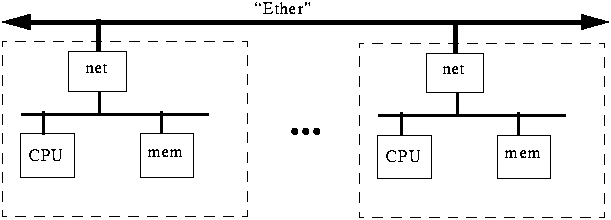
Broadcast Networks (e.g., Ethernet)

Broadcast Networks
Broadcast networks (Fig 25.2 are categorised by:
-> CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense, Multiple Access/Collision Detection).
Token rings
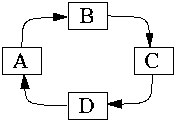
Token rings
Token rings (Fig 25.3 are categorised by:
To transmit, a station grabs the token, transmits, releases the token.
Regulates access to networks by only allowing one unit to broadcast at a time.
A station can transmit a frame at a given priority if it can grab a token with an equal or lower priority. Otherwise, make reservation.
FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)
It has a dual ring topology with primary ring for data transmission and secondary ring for fault tolerance (See Figure 10.3 from the Steinmetz and Nahrstedt book.)
The synchronous mode enables bandwidth reservation and the asynchronous mode is similar to the Token Ring protocol.
-> circuit switched services (isochronous services) for delay-sensitive applications, e.g., audio and video; and packet switched services (synch and asynch) for others in the same network.