


Next: Lossless Compression Algorithms (Repetitive
Up: Classifying Compression Algorithms
Previous: Classifying Compression Algorithms
Compression basically employs redundancy in the data:
- Temporal -- in 1D data, 1D signals, Audio etc.
- Spatial -- correlation between neighbouring pixels or data items
- Spectral -- correlation between colour or luminescence components.
This uses the frequency domain to exploit relationships between frequency
of change in data.
- psycho-visual -- exploit perceptual properties of the human visual
system.
Compression can be categorised in two broad ways:
- Lossless Compression
- -- where data is compressed and can be
reconstituted (uncompressed) without loss of detail or information. These
are referred to as bit-preserving or reversible compression systems also.
- Lossy Compression
- -- where the aim is to obtain the best possible
fidelity for a given bit-rate or minimizing the bit-rate to achieve
a given fidelity measure. Video and audio compression techniques are most
suited to this form of compression.
If an image is compressed it clearly needs to uncompressed (decoded)
before it can viewed/listened to. Some processing of data may be possible
in encoded form however.
Lossless compression frequently involves some form of entropy
encoding and are based in information theoretic techniques (Fig. 7.1)
Lossy compression use source encoding techniques that may involve
transform encoding, differential encoding or vector quantisation (Fig. 7.1).
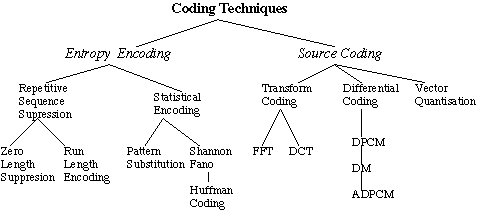
Classification of Coding Techniques
We now address common coding methods of each type in turn:



Next: Lossless Compression Algorithms (Repetitive
Up: Classifying Compression Algorithms
Previous: Classifying Compression Algorithms
Dave Marshall
10/4/2001

