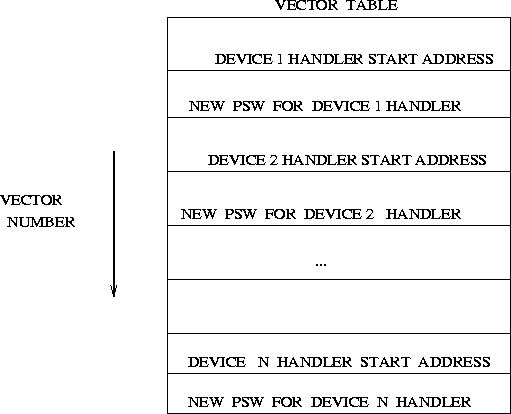
Figure:
if all interrupt handling in assembly language, in the Kernel, then interrupt handlers :
Note : Interrupt handlers should however be written in
a high level language, and be part of device handler process -
particularly valid for real time systems.
Also, LIH in kernel to perform actions common to all interrupt
handling.
Note: There is a slight distinction between forking a thread
as opposed to forking a process (unix 'fork'). A Unix fork creates a
new process, so it has to create a new address space, in addition
to a new thread.
Forking a thread is very much like an asynchronous procedure call,
it means - go do this work - where the calling thread does not wait
for the callee to complete.
What if the calling thread needs to wait ?
Thread Join - wait for a forked thread to finish.
Hence, a traditional procedure call (in Pascal for instance) :
procedure A() B() procedure B() equivalent to procedure A() Thread t = new Thread ; t^Fork(B) ; t^Join()