


Next: Monolithic - 'the BIG
Up: No Title
Previous: Kernel functions
Kernel is invoked as a result of :
- External interrupt - such as a device (printer, disk drive,
kettle) or a timer (clock).
- Internal interrupt - error condition (such as divide by zero,
memory protection violation, page fault, execution of an illegal or
previledged instruction etc).
- Kernel call from a running process.
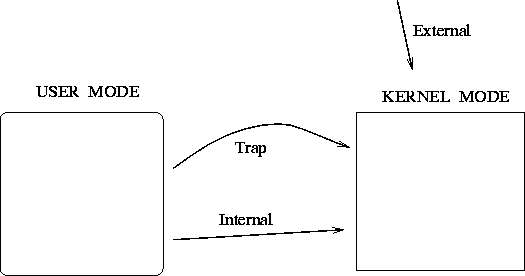
Figure:
Kernel entry switches processor into previledged mode
Access to :
- Kernel general purpose registers
- Program status word
- Memory management registers
- I/O instructions (on some processors)
- Enable and disable of interrupts
- Special instructions (such as halt)
Note: some system processes may need to execute in previledged
mode (such as device handlers).
How is kernel entered from a user processes
- Procedure Calls
- Special Instructions (such as Supervisor Call (SVC) or trap)
- Message passing (as in Mach)
For procedure call, Kernel resides in shared address space (or ROM)
and
a) Kernel procedures are linked into process code
b) Single entry point into kernel, and parameters indicate kernel operation
The special instructions are similar to hardware interrupts, and register
parameters determines operation.
In a message passing case, each process has default ports for sending and receiving
messages to or from the Kernel.
Where are the kernel parameters stored ?
On the Kernel stack, which is used for variable and parameter passing
within the Kernel.
- Kernel has a stack like any other process - kernel registers
- Two stacks are per process - a user mode and a kernel mode stack,
however, this required extra memory (Unix)
- Kernel runs on a user stack (as done in monitors), but in this case
it is possible that the data may become corrupted



Next: Monolithic - 'the BIG
Up: No Title
Previous: Kernel functions
Omer F Rana
Thu Feb 6 16:13:26 GMT 1997
