
Brif Introduction
Alan Mathison Turing was an English mathematician and logician. He is known as the father of computer science and the father of artificial intelligence at the same time. In 1931, Turing entered King's College Cambridge, and after graduation, he went to Princeton University in the United States to study for a doctorate, returned to Cambridge after the outbreak of World War II, and later assisted the military to crack the famous German cipher system Enigma, helping the Allies win World War II. A lifetime of creating a wealth of treasures for omputer science.
Great Achievements
(1)"Universal Turing machine" (UTM) --- the germ of a new concept
The general-purpose computer of 1936, today simply known as the "Universal Turing Machine" (UTM), was an abstract conceptual model in which different programs fed onto tape allowed it to perform different tasks. This was Turing's original idea: a single, fixed-structure machine, by utilizing instructions stored in its memory, could, like a chameleon, turn itself into a machine dedicated to performing a task and another machine dedicated to performing another task. The idea seems obvious today, but at the time, when engineers considered making different machines for different purposes, the concept was not only original, but revolutionary ((Anguera et al. 2020). Later, Turing defined the computable function as the computable function of the Turing machine, and proposed the concept of a universal Turing machine, which is equivalent to the interpreter program of the general computer, which directly promoted the design and development of the later general computer.

(Lara et al. 2020)
(2)The proposal of the Turing test --- the germ of artificial intelligence
Refers to the situation that the tester is separated from the test subject (a person and a machine), and asks the test subject questions at will through some devices (such as a keyboard). After multiple tests, if the machine asks each participant to make more than 30 percent of the misjudgments, the machine passes the test and is considered to have human intelligence. The Turing test proposes a test method for determining whether a machine has intelligence, and is now often one of the most important criteria for testing whether artificial intelligence products meet the requirements.
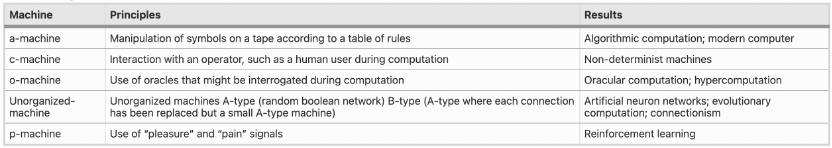
(3) The corresponding value embodiment of the basic principles proposed by Turing in the field of computer science
He develops different machines to provide different learning and self-processing models, such as simulating artificial neuron networks, evolutionary computation, and reinforcement learning. The following table shows the various machines and principles developed by Turing and their corresponding contributions to the field of computer science.
 (Lara et al. 2020)
(Lara et al. 2020)
contact
Write down some thoughts about CT (this would be send to personal emil address):
This website was designed by Cardiff University student(MSC computing--Tianyu Hu C22077355)