


Next: Reasoning in Bayesian nets
Up: Bayesian networks
Previous: Bayesian networks
- A Bayesian Network is a directed acyclic graph:
- A graph where the directions are links which indicate dependencies that
exist between nodes.
- Nodes represent propositions about events or events themselves.
- Conditional probabilities quantify the strength of dependencies.
Consider the following example:
- The probability,
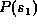 that my car won't start.
that my car won't start.
- If my car won't start then it is likely that
- The battery is flat or
- The staring motor is broken.
In order to decide whether to fix the car myself or send it to the garage I
make the following decision:
- If the headlights do not work then the battery is likely to be flat so i
fix it myself.
- If the starting motor is defective then send car to garage.
- If battery and starting motor both gone send car to garage.
The network to represent this is as follows:
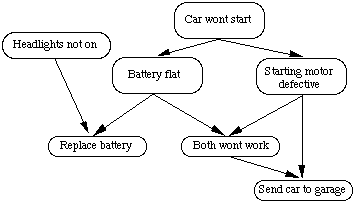
Fig. 21 A simple Bayesian network
dave@cs.cf.ac.uk
