


Next: Problem solving and reasoning
Up: Blackboard systems
Previous: Knowledge organisation and reasoning
The above example illustrates some problems that may arise when implementing a
blackboard system. In this section we consider some general considerations
needed when implementing and designing a blackboard framework.
Knowledge sources
- Domain knowledge should be divided up so that sources are kept separate
and independent.
- Each knowledge source is responsible for knowing the conditions under
which it can contribute a solution:
- A set of preconditions are specified that must be satisfied before the
source can be activated.
- Knowledge sources are represented as sets of rules, procedures or logic
assertions.
- Knowledge sources only modify blackboard or control data structures. And
only knowledge sources modify the blackboard (Fig 23).
Blackboard data structure
- Knowledge sources produce changes to this structure that lead
incrementally to a solution.
- The data structure consists of objects from the solution space:
- input data,
- partial solutions,
- alternatives,
- final solutions,
- control data.
- Final form of structure is problem dependent although objects are
hierarchically organised
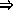 tree/graph type structure.
tree/graph type structure.
- multiple hierarchies or blackboard panels are permitted.
Control
- The focus of attention can either be:
- blackboard structures, or
- knowledge sources, or
- both.
- Solutions built up on step at a time. Many kinds of reasoning (e.g.
data driven, goal driven, expectation driven) have been applied.



Next: Problem solving and reasoning
Up: Blackboard systems
Previous: Knowledge organisation and reasoning
dave@cs.cf.ac.uk