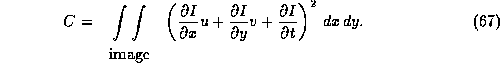
The above smoothness
constraint is not necessarily entirely consistent with the optical
flow constraint. We can express how much a solution for u and v
deviates from the condition required by the optical flow
constraint equation by evaluating
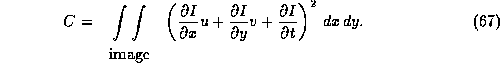
To meaningfully combine these two constraints, we use the technique of Lagrangian multipliers:
Minimising the resulting integral can be done by using standard techniques from the calculus of variations, which show that the functions u and v which are required satisfy the coupled pair of differential equations:
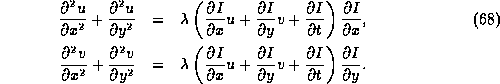
The derivatives of I for each pixel are obtained
from the original image, and ![]() is chosen as above. An
iterative method can then be used to solve these equations for
u and v at each pixel.
is chosen as above. An
iterative method can then be used to solve these equations for
u and v at each pixel.