

Next: Optical Flow
Up: Relaxation Labelling
Previous: Relaxation Labelling
Relaxation methods
have been particularly applied to optimisation
problems. Such problems are very common in
computer vision and so relaxation methods have been
applied in a wide variety of ways to computer vision.
Relaxation methods have been applied to:
- Edge linking
- -- The
probabilities of edge points lying on particular edges is
determined by considering neighbouring edge points. Different
labels are used for each edge, and a relaxation schedule is then
used to find the appropriate label for each edge point.
- Line labelling techniques
-
can be expressed a relaxation problem.
- Label lines
as belonging to a certain class of edge (occluding,
concave or
convex).
- Probabilities can be assigned to
each type of
labelling fairly easily.
- Only certain sets of
edge labellings are mutually compatible at line junctions.
- These
restrictions can be expressed as constraints when the conditional
probabilities for the particular labels are estimated.
- Segmentation
- can be interpreted in two
slightly different ways here:
- The process of grouping pixels into regions of
similarity. Here the relaxation processes amount to
self-organisation of the image. The regions are simply
labelled as
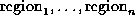 .
.
- The process of labelling regions of image as belonging to
recognised physical entities such as sky, grass, trees,
car and road.
 David Marshall 1994-1997
David Marshall 1994-1997
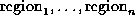 .
.