


Next: Digital Video
Up: Basics of Video
Previous: Types of Colour Video
The following figures (Fig. 6.27 and 6.28) are from A.M. Tekalp,
Digital video processing, Prentice Hall PTR, 1995.
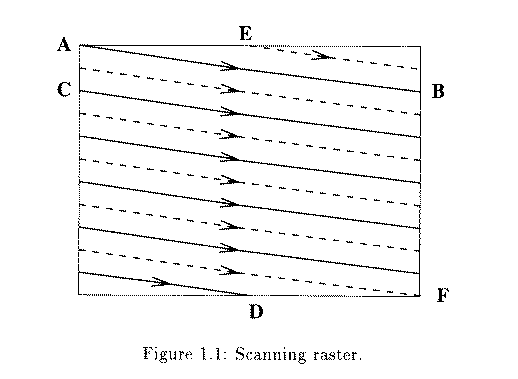
Raster Scanning
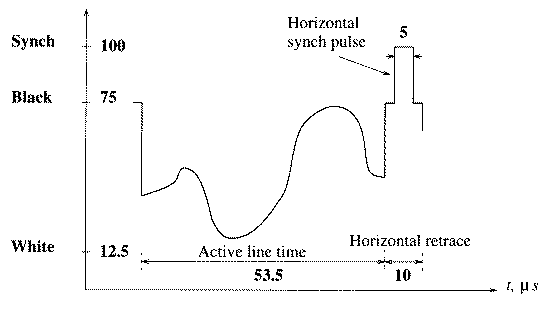
NTSC Signal
NTSC Video
- 525 scan lines per frame, 30
frames per second (or be exact, 29.97 fps, 33.37 msec/frame)
- Aspect ratio 4:3
- Interlaced, each frame is divided into 2 fields, 262.5 lines/field
- 20 lines reserved for control information at the beginning
of each field (Fig. 6.29)
- So a maximum of 485 lines of visible data
- Laserdisc and S-VHS have actual resolution of 420 lines
- Ordinary TV - 320 lines
- Each line takes 63.5 microseconds to scan. Horizontal retrace
takes 10 microseconds (with 5 microseconds horizontal synch pulse
embedded), so the active line time is 53.5 microseconds.
Digital Video Rasters
- Colour representation:
- NTSC uses YIQ colour model.
- composite = Y + I cos(Fsc t) + Q sin(Fsc t), where
Fsc is the frequency of colour subcarrier
- Eye is most sensitive to Y, next to I, next to Q. In NTSC, 4 MHz is
allocated to Y, 1.5 MHz to I, 0.6 MHz to Q.
PAL Video
- 625 scan lines per frame, 25
frames per second (40 msec/frame)
- Aspect ratio 4:3
- Interlaced, each frame is divided into 2 fields, 312.5 lines/field
- Colour representation:
- PAL uses YUV (YCbCr) colour model
- composite = Y + 0.492 x U sin(Fsc t) + 0.877 x V cos(Fsc t)
- In component analog video, U and V signals are lowpass filtered
to about half the bandwidth of Y.



Next: Digital Video
Up: Basics of Video
Previous: Types of Colour Video
Dave Marshall
10/4/2001



