


Next: Conversion between RGB and
Up: Colour in Image and
Previous: CRT Displays
- A black and white image is a 2-D
array of integers.
- A colour image is a 2-D array of (R,G,B) integer triplets.
These triplets encode how much the corresponding phosphor should be
excited in devices such as a monitor.
- Example is shown in Fig 6.23.

Display of a Colour Cube
Beside the RGB representation, YIQ and YUV are the two commonly used
in video.
YIQ Colour Space
- YIQ is used in colour TV
broadcasting, it is downward compatible with B/W TV.
- Y (luminance) is the CIE Y primary.
Y = 0.299R + 0.587G + 0.114B
- the other two vectors:
I = 0.596R - 0.275G - 0.321B
Q = 0.212R - 0.528G + 0.311B
- The YIQ transform:
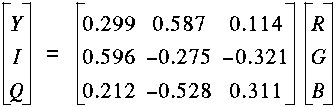
YIQ Transform of a colour image
- I is red-orange axis, Q is roughly orthogonal to I.
- Eye is most sensitive to Y, next to I, next to Q.
In NTSC, 4 MHz is allocated to Y, 1.5 MHz to I, 0.6 MHz to Q.
- An Example YIQ Decomposition is shown in Fig. 6.24.

Example YIQ Decomposition
CCIR 601 (YUV)
The CMY Colour Model
- Cyan, Magenta, and
Yellow (CMY) are complementary colours of RGB (Fig. 6.26). They can be used as
Subtractive Primaries.
- CMY model is mostly used in printing devices where the colour
pigments on the paper absorb certain colours (e.g., no red light
reflected from cyan ink).
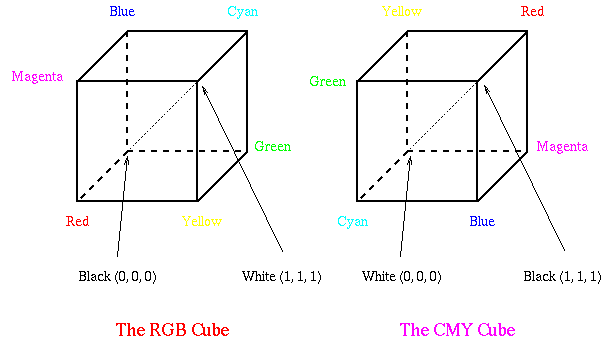
The RGB and CMY Cubes



Next: Conversion between RGB and
Up: Colour in Image and
Previous: CRT Displays
Dave Marshall
10/4/2001


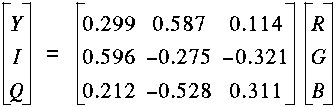

![$\left[ \begin{array}
{c}Y\ U\ V\end{array} \right] =
\left[ \begin{array}
{r...
...081 \end{array} \right]
\left[ \begin{array}
{c}R\ G\ B\end{array} \right] $](img6.gif)

